Effective communication is essential for delivering quality healthcare. Patients who grasp their diagnoses, treatment options, and care instructions are more likely to adhere to treatments and actively participate in their care, leading to improved health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system. Yet, patients with limited English proficiency (LEP) and disabilities often face significant barriers in accessing essential communication.
With the implementation of the CMS 2024 Final Rule (RIN 0938-AU96) in January 2024, healthcare providers and insurers are still navigating these changes, striving to understand and implement the necessary adjustments to their processes. Take action and stay ahead with clear communication and accessible healthcare materials for diverse patient populations, aiming to create a more inclusive healthcare system.
objectives of the 2024 Medicare Advantage and Part D Final Rule
The CMS 2024 Final Rule is a game-changer for providers and insurers in the Medicare Advantage network and LEP members of these plans. It sets the stage for increased accountability, streamlined processes, and reinforced penalties for non-compliance. Several provisions in the new rule specifically address the need for enhanced translation and interpretation services, pivotal for achieving health equity.
changes to translation and interpretation requirements
language access: Providers must now offer comprehensive language services for all interactions with LEP patients, ensuring they can understand and engage in their healthcare across all settings.
improved translation and accessibility standards: Interpreters and translators must meet specific qualifications and standards, including proficiency in medical terminology and cultural competence, to ensure high-quality language services.
qualified interpreters and translators: Providers are now required to offer professional interpreters and translators proficient in English, the target language, and medical terminology to ensure accuracy and cultural relevance. A key aspect of the new rule is that family members can no longer serve as interpreters. The dangers and concerns associated with this practice are significant, including potential miscommunication and breaches of patient confidentiality.
cultural competency: Encouraging providers to integrate cultural competency training into their practice enhances communication and understanding with patients from diverse backgrounds, fostering trust and better health outcomes.
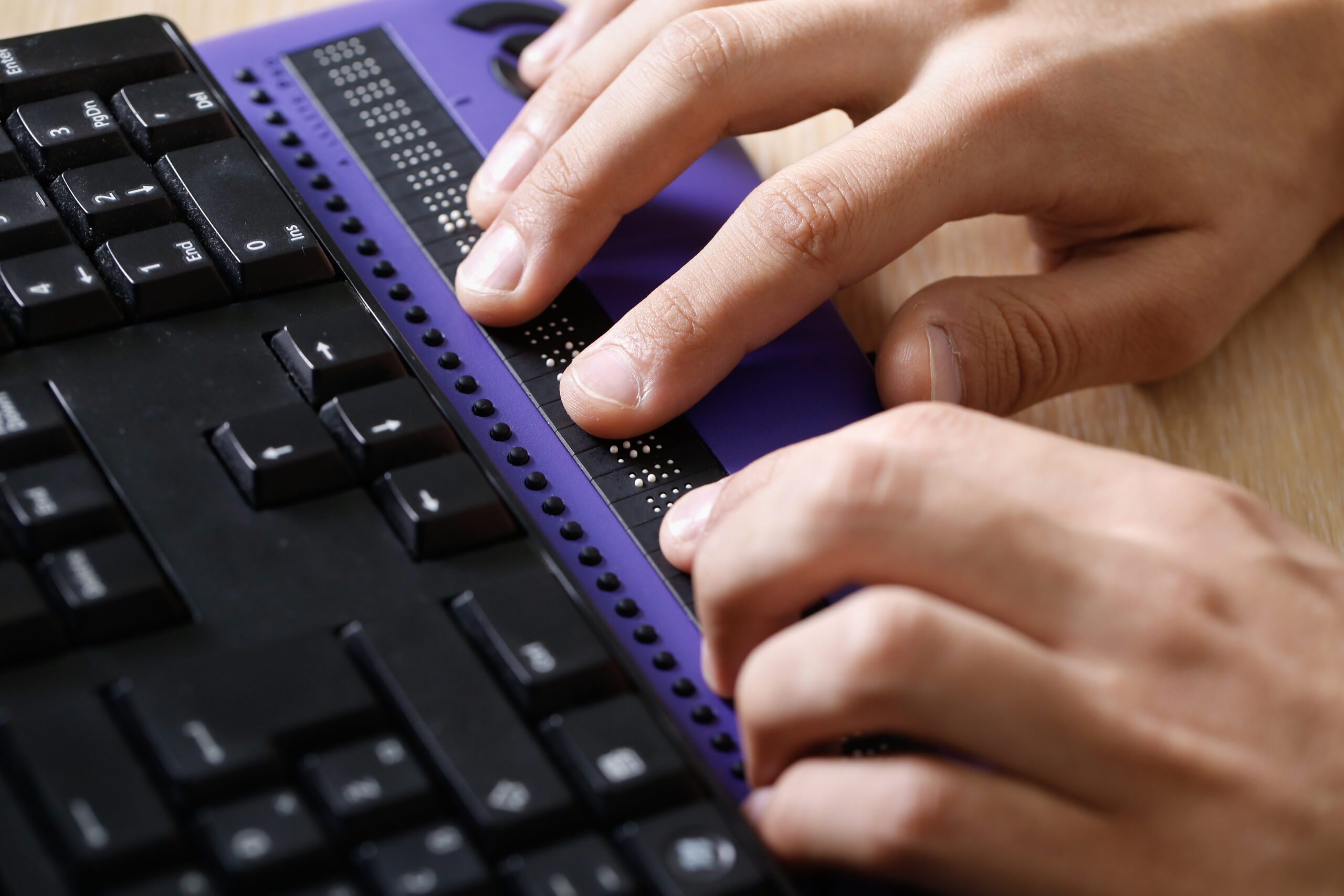


changes to accessible format requirements
accessibility: Providers must offer information in accessible formats such as Braille, large print, audio, and electronic formats compliant with WCAG 2.0 standards, ensuring equitable access for patients with disabilities.
alternative formats: Prompt provision of alternative formats is essential, ensuring beneficiaries with disabilities receive the necessary information without delay.
electronic health records (EHRs): Accessibility standards now extend to EHRs, ensuring individuals with disabilities can independently access their health information seamlessly.
the significance of language services in achieving health equity
- enhanced language assistance services
- culturally competent care
- accessibility of language services
-
monitoring and reporting
impact of language services on star ratings
The availability and quality of language services directly affect the Star Ratings for Medicare Advantage and Part D plans. These ratings measure the quality of health and drug services received by consumers, including the availability of foreign language interpreters and TTY services. Compliance with these measures is essential for a high Star Rating, reflecting a plan’s commitment to providing accessible and high-quality services to all beneficiaries.
To ensure individuals with LEP and disabilities can make informed healthcare decisions, the rule enforces additional Medicare marketing and communication standards. Providing clear, accurate information in non-English languages and accessible formats is crucial for removing ambiguity and protecting consumers.
The CMS 2024 Final Rule marks a significant step forward in enhancing language access and communication in healthcare. By addressing translation and accessible format requirements, the rule aims to improve care quality and information accessibility for all patients. Healthcare providers must adapt to these changes, investing in language services, upgrading technology, and prioritizing training initiatives to ensure compliance and provide equitable, inclusive healthcare services.
As your partner in language solutions, CQ fluency is here to help healthcare providers meet these new standards. Our team of qualified translators and accessibility experts ensures culturally relevant and linguistically accurate translations, helping you navigate the complexities of the CMS 2024 Final Rule. Contact us today to learn how we can assist with your language and accessibility needs, ensuring every patient receives the care they deserve.
